Setup And Overview
Kotlin DataFrame Compiler Plugin is a Kotlin compiler plugin that automatically generates
type-safe extension properties for your dataframes,
allowing you to access columns and row values in a type-safe way and avoid mistakes in column names.
Why use it?
Access columns as regular properties:
df.nameinstead ofdf["name"].Get full IDE and compiler support: autocompletion, refactoring, and type checking.
Improve code readability and safety when working with DataFrame.
Check out this video that shows how expressions update the schema of a dataframe:
Setup
We recommend using an up-to-date IntelliJ IDEA and Kotlin version for the best experience. Requires at least versions 2025.2 and 2.2.20, respectively.
Setup plugins in build.gradle.kts:
Setup library dependency:
Due to the known issue, incremental compilation must be disabled for now. Add the following line to your gradle.properties file:
Sync the project.
The DataFrame compiler plugin can be used in Maven projects starting from IntelliJ IDEA 2025.3, available now as EAP builds
Setup plugin in pom.xml:
Setup library dependency:
Sync the project.
Features overview
Static interpretation of DataFrame API
Plugin evaluates dataframe operations, given compile-time known arguments such as constant String, resolved types, property access calls. It updates the return type of the function call to provide properties that match column names and types. The goal is to reflect the result of operations you apply to dataframe in types and have convenient typed API
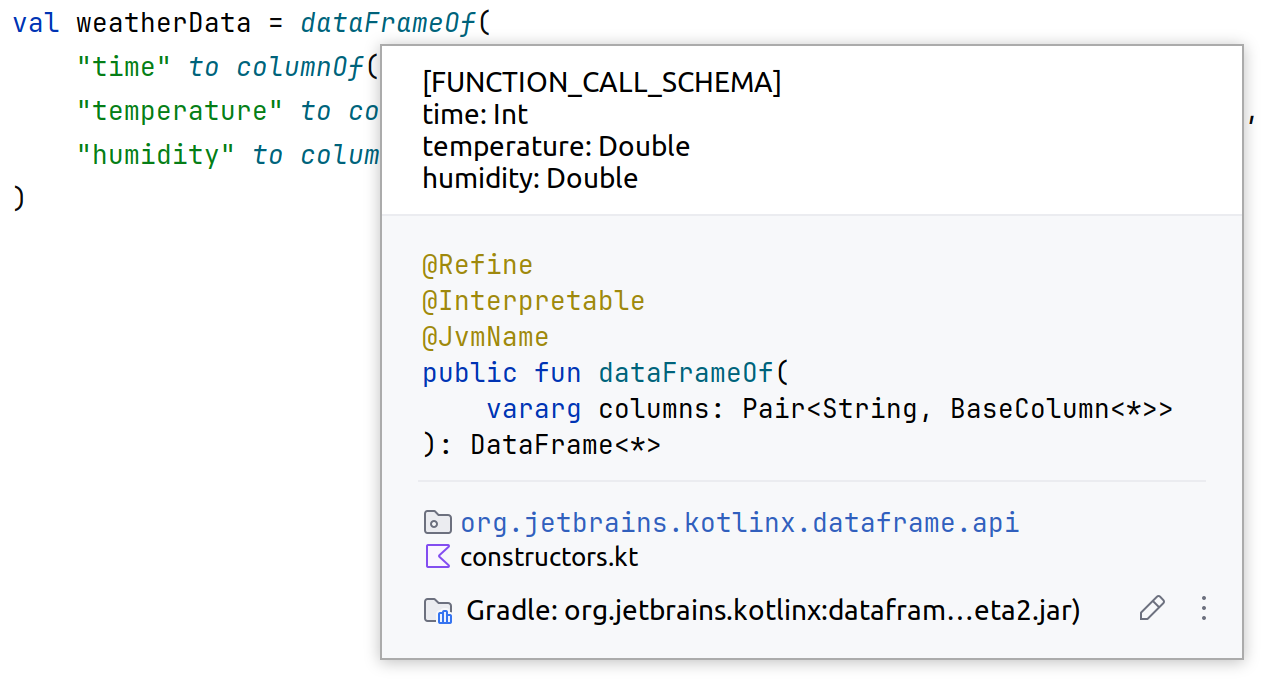
The schema of DataFrame, as the compiler plugin sees it, is displayed when you hover on an expression or variable:
@DataSchema declarations
Untyped DataFrame can be assigned a data schema - top-level interface or class that describes names and types of columns in the dataframe.
Learn more about data schema declarations
Examples
Kotlin DataFrame in the IntelliJ IDEA Gradle project example
— an IntelliJ IDEA Gradle project showcasing simple DataFrame expressions using the Compiler Plugin.Kotlin DataFrame in the IntelliJ IDEA Maven project example
— an IntelliJ IDEA Maven project showcasing simple DataFrame expressions using the Compiler Plugin.Compiler Plugin Examples — few examples of Compiler Plugin usages.